ResearchGate has highlighted a novel co-packaged design utilizing high-density interconnects in a recently published schematic. The design aims to improve efficiency and performance in integrated circuits, potentially impacting future technology in microelectronics. Further details of the design’s architecture and potential applications can be found on ResearchGate’s platform.
Category: Blog
Your blog category
-

Stylish Anime-Inspired Glasses Designs Unveiled: Fandom Meets Fashion
Gunnar Optiks has launched its anime-inspired glasses Fall Collection, featuring three new designs born from their collaboration with tokidoki. The collection blends pop culture themes with an autumnal aesthetic, emphasizing playful and whimsical style. Each pair of glasses is equipped with Gunnar’s signature lens technology, engineered to block blue light and UV light. This feature is designed to reduce eye strain and discomfort commonly associated with extended screen use, such as dry eyes, blurred vision, and headaches. Beyond their fashionable appearance, each glasses style is bundled with functional accessories designed by tokidoki founder Simon Legno, including a hard case, a microfiber pouch, and a cleaning cloth. Additional features of the eyewear include flexible spring hinges, anti-reflective coatings, and hypoallergenic nose pads.
-
Ford Stops ‘Selfie Spies’ with Optical Illusions Protecting Car Designs
Ford is using optical illusions to safeguard its secret car designs from prying eyes, especially those of “selfie spies” attempting to capture confidential details with their phones. This innovative method, inspired by techniques used to protect banknotes and documents, involves applying intricate patterns to prototypes. These patterns create optical illusions in photographs, distorting the true shapes and lines of the vehicle, making it difficult to discern design features from images, particularly those taken casually by onlookers. Ford believes this approach will significantly hinder industrial espionage and protect their design innovations from premature leaks.
-
TECNO Unveils Starry Optical Fiber Tech for Stunning Phone Designs
TECNO recently showcased its Starry Optical Fiber technology, a new innovation aimed at bringing unique and visually striking designs to smartphones. This technology allows for intricate light patterns and textures to be embedded within the phone’s back panel, creating a distinctive aesthetic. The company demonstrated the capabilities of this technology, suggesting it could be implemented in future TECNO devices. Starry Optical Fiber tech opens possibilities for phone manufacturers to move beyond traditional materials and design approaches, potentially offering consumers more personalized and visually appealing mobile devices. While specifics on when and in which models this technology will debut are still awaited, this unveiling signals TECNO’s commitment to innovative design in the competitive smartphone market.
-
Here are a few options for news article titles, all under 13 words, based on "Just a moment…":
- Brief Pause: News Update Coming in Just a Moment (9 words)
- Momentary Delay: Stay Tuned for Developing Story (8 words)
- Impending Announcement: A Momentary Pause Before News (9 words)
- Hold On: Important Information Coming Just a Moment (9 words)
- Anticipation Builds: "Just a Moment" Before Reveal (8 words)
Choose whichever best fits the context you have in mind!
Website visitors are encountering a new interactive security measure requiring them to verify their humanity. Users attempting to access content are being presented with a page featuring a button that must be pressed and held until it turns green. This step is described as necessary to confirm that the user is human due to what the system deems an “unusual request.” The page instructs users to “Press and Hold” the button and indicates progress with a status message. For those who believe they have encountered this verification in error, a link to the website’s support team is provided for assistance.
-
Researchers Simulate Better All-Optical NOR Gate Using Semiconductor Amplifier
Researchers have simulated a novel design for an all-optical NOR gate, a fundamental component for future optical computing systems. This research centers on enhancing the ‘extinction ratio’ of the gate, a crucial factor for ensuring clear and dependable signal processing within optical circuits. Utilizing a semiconductor optical amplifier in their design and employing computer simulations, the researchers demonstrated a marked improvement in the gate’s capacity to distinguish between ‘on’ and ‘off’ light signals. This enhanced performance represents a significant stride towards the development of more efficient and robust optical computing technologies, potentially paving the way for faster data processing and communication capabilities.
-

New Math Technique Sharps Vision in Optical Systems
Scientists have developed a novel mathematical approach using Lie algebraic methods to analyze and correct optical distortions, offering a significant advancement in optical design. This new method, pioneered by researcher Barion, provides a more efficient alternative to traditional computer simulations, which can be time-consuming and may not always reveal the fundamental causes of aberrations.
Barion’s research introduces mathematical formulas based on Lie algebra to describe the behavior of light passing through optical elements like lenses and mirrors. These formulas provide a deeper understanding of aberrations and simplify the design of optical systems that minimize distortions.
While complex optical devices may still require computer-based optimization, Barion’s analytical methods offer a robust starting point, streamlining the design process. The implications of this work are wide-ranging, particularly benefiting fields such as astronomy, where sharp images of distant galaxies are essential, and medical imaging, where precise optics are critical for diagnostic accuracy. Furthermore, the research has the potential to improve fiber optic communication by reducing signal loss and enhance everyday technologies like smartphone cameras and virtual reality headsets. This mathematical advancement promises to pave the way for the development of next-generation, high-precision imaging technology by providing a new and effective way to optimize optical system performance.
-
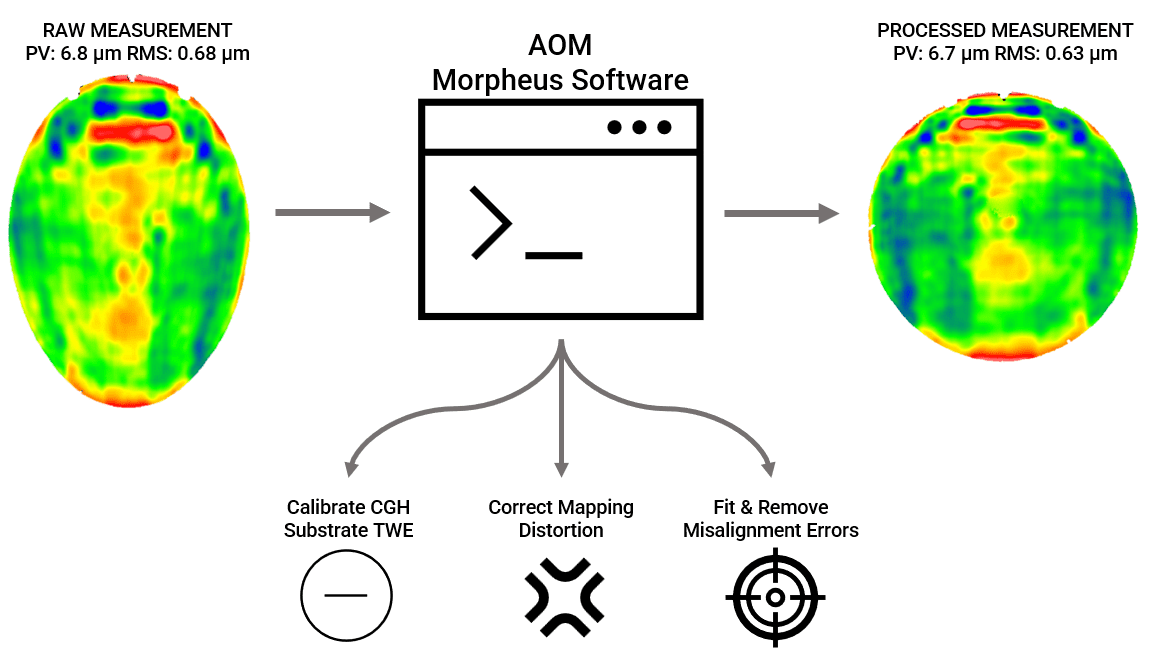
AOM Unveils Data Reduction Software in January
Arizona Optical Metrology (AOM) has launched its Morpheus™ software, designed for uncertainty analysis and data reduction in computer-generated hologram (CGH) testing. The software is intended to improve deterministic polishing or machining of optics by providing comprehensive analysis of CGH design residuals, as-built CGH attributes, test geometry, and alignment tolerances, as well as measurement noise. Morpheus™ quantifies total test uncertainty and compensates for substrate variations in as-built CGHs. It also includes features for mapping correction of surface figure errors in the unit under test’s lateral coordinates and for analyzing and removing measurement errors caused by misalignment in CGH tests.
-
Novel Conditional Invertible Neural Network Architecture Proposed by Researchers
Researchers have presented an overview of a proposed conditional invertible neural network (cINN), detailing its complete derivation and exploring novel applications. This work, highlighted on ResearchGate, delves into the architecture and mathematical foundations of cINNs, a type of neural network that allows for both forward and reverse computations. The research emphasizes the comprehensive derivation of the cINN model and investigates its potential in various innovative applications. The overview serves as an introduction to the capabilities and theoretical underpinnings of this specific cINN implementation, suggesting advancements in the field of invertible neural networks and their practical uses.
-
Here are a few options for a news article title based on the scientific title, keeping it under 13 words and suitable for a news format:
Option 1 (Focus on benefit):
New Light Probes Help Surgeons See Tumors More Clearly
Option 2 (More technical, but concise):
Enzyme ‘Smart’ Probes Light Up Tumors for Better Cancer Surgery
Option 3 (Focus on the mechanism in simpler terms):
‘Smart’ Light Probes Use Enzymes to Highlight Tumors in Surgery
Option 4 (Shortest and most impactful):
New ‘Smart’ Light Probes Aid Precise Tumor Surgery
All of these options are under 13 words and convey the main idea of the scientific paper in a news-oriented style. Option 1 is perhaps the most broadly accessible. Option 4 is the most concise. Let’s go with Option 1 for broader appeal.
Final Answer:
New Light Probes Help Surgeons See Tumors More Clearly
Researchers have engineered a new class of optical contrast agents designed to improve the precision of fluorescence-guided surgery, particularly for cancer. These agents are activated by proteases, enzymes often found at elevated levels in tumor environments, allowing for selective targeting of cancerous tissue. The innovation lies in the agents’ “latent lysosomotropic effect,” meaning they are designed to accumulate within lysosomes, cellular compartments within tumor cells. This accumulation enhances the fluorescent signal specifically at the tumor site, potentially providing surgeons with a clearer and more detailed view of tumor margins during surgery. Traditional contrast agents can sometimes lack specificity or sufficient accumulation in tumors, hindering precise tumor removal. This new approach aims to overcome these limitations by creating agents that are not only activated by tumor-associated proteases but also become trapped within tumor cells, leading to brighter and more specific fluorescence, ultimately assisting surgeons in distinguishing between cancerous and healthy tissue with greater accuracy. The development holds promise for improving surgical outcomes and potentially reducing cancer recurrence by ensuring more complete tumor resection.