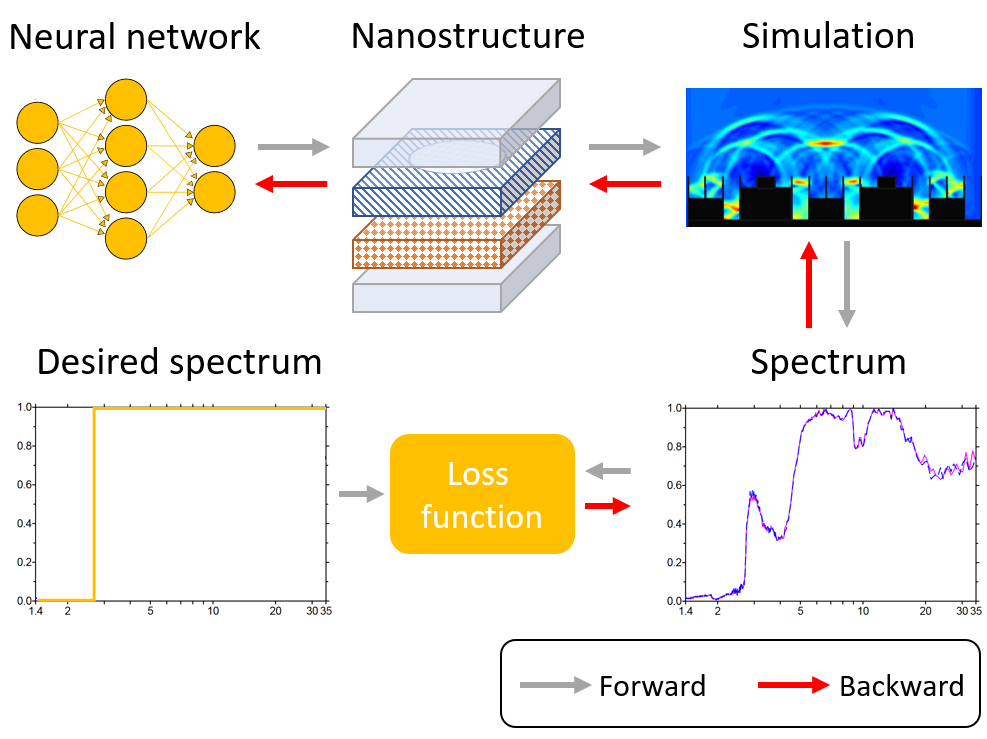
Spacecraft utilize optical solar reflectors on their exterior surfaces to regulate temperature in space. These reflectors serve a critical dual purpose: deflecting incoming sunlight and emitting infrared radiation, effectively managing heat from both solar exposure and onboard equipment. For many years, quartz tiles coated with metal have been the standard for these reflectors. However, these traditional designs are heavy, expensive, and prone to damage. Flexible polymer alternatives exist but lack the performance and durability of quartz. To overcome these limitations, scientists are innovating with new materials and designs for reflectors. These include metamaterials, which are engineered to have special optical properties, and thermochromic materials that adjust heat emission based on temperature. To speed up the development process, researchers are employing machine learning techniques, specifically a method called inverse design. This involves using neural networks to determine the ideal material properties for optimal reflector performance, a more efficient approach compared to traditional trial-and-error methods. The aim is to create high-performance reflectors with wider design possibilities for future spacecraft. Currently, this research is ongoing, with initial findings being analyzed. Scientists are also exploring potential applications of this technology beyond reflectors, including advanced solar sails for spacecraft propulsion. In the interest of open research, all data and code from this project will be made publicly accessible.
Option 1 (Focus on Key Innovation):
Inverse Design Improves Nanotech Solar Reflectors Optics
Option 2 (Slightly more broadly accessible):
Inverse Design Breakthrough for Nanostructured Solar Reflectors
Option 3 (Emphasize the advancement):
Inverse Design Advances Nanostructured Optical Solar Reflectors
Option 4 (Concise and direct):
Nanostructured Solar Reflectors Optimized by Inverse Design
Leave a Reply