ScienceDirect is prompting users to ensure their web browsers are up to date to properly access the platform’s content. A message displayed on the site indicates that some users may be viewing it with an outdated browser version, potentially impacting their experience. ScienceDirect is directing individuals to a page outlining compatible browsers and suggesting they update if necessary for optimal viewing.
News
-
ScienceDirect Restricts Access to Research Pages
Try TracePro Software for design and analysis of illumination and optical systems.
-
New Wavefront Lens Design Corrects Presbyopia; Clinical Classification Unveiled
Researchers have developed a novel intraocular lens designed to correct presbyopia, the age-related loss of near vision. The lens utilizes a wavefront-shaping optical design. Details on the specific optical design characteristics and clinical performance are outlined in a newly published study. This new intraocular lens represents a potential advancement in surgical options for individuals seeking to address presbyopia and improve their vision at all distances after cataract surgery. The research further proposes a clinical classification system for this type of lens based on its optical properties and performance.
Try TracePro Software for design and analysis of illumination and optical systems.
-

IBM Unveils New Optical Character Recognition Technology
Researchers have developed innovative techniques for generating synthetic data to overcome the challenges of training computer vision systems, particularly for document analysis tasks. This approach addresses the difficulty of obtaining large, accurately labeled datasets, which are crucial for training effective models. By synthesizing data, developers gain precise control over data characteristics like font, color, size, background noise, and labeling granularity. This level of control is proving crucial for enhancing model accuracy and enabling the recognition of complex document elements such as punctuation, layout, handwriting, and form structures. The use of synthetic data has already led to a significant upgrade in a core Optical Character Recognition (OCR) model, resulting in improved accuracy and faster processing speeds. Beyond OCR, this synthetic data methodology is now being applied to a wider range of applications including object segmentation, text recognition, natural language processing for grammar correction, entity grouping, semantic classification, and entity linkage, demonstrating its broad potential across various artificial intelligence domains.
Try TracePro Software for design and analysis of illumination and optical systems.
-
Systematic Microscope Objective Design Review and Analysis Published
Researchers have published a study detailing a systematic approach to designing microscope objectives. The first part of this research focuses on a comprehensive review of existing objective systems and an in-depth analysis of their design principles. This work lays the foundation for future advancements in microscope objective technology through a structured and analytical design process.
Try TracePro Software for design and analysis of illumination and optical systems.
-

Here are a few options for the news article title, all under 13 words:
Option 1 (Focus on launch):
Siemens Launches SIMATIC MV for Lightning-Fast Reading
Option 2 (More descriptive):
Siemens SIMATIC MV Vision System: Lightning-Fast Reading at Your Command
Option 3 (Slightly shorter and punchy):
Siemens SIMATIC MV: Lightning-Fast Reading System Debuts
Option 4 (Highlighting speed and control):
Siemens SIMATIC MV for Lightning-Fast, Controlled Reading
Option 5 (Concise and impactful):
Lightning-Fast Reading: Siemens Unveils SIMATIC MV Vision
The best and most news-article style within the word limit, and closest to the original meaning while being newsy, is Option 4:
Siemens SIMATIC MV for Lightning-Fast, Controlled Reading
Siemens has announced advancements in its SIMATIC MV vision system, emphasizing significantly improved reading speeds. The system is now capable of exceptionally fast data capture, crucial for high-throughput industrial applications. This enhanced performance allows for quicker processing and analysis within automated production lines, streamlining operations where rapid identification and verification of codes and characters are essential. The upgrade aims to boost efficiency and productivity in manufacturing and logistics environments by minimizing delays associated with vision-based data acquisition.
Try TracePro Software for design and analysis of illumination and optical systems.
-
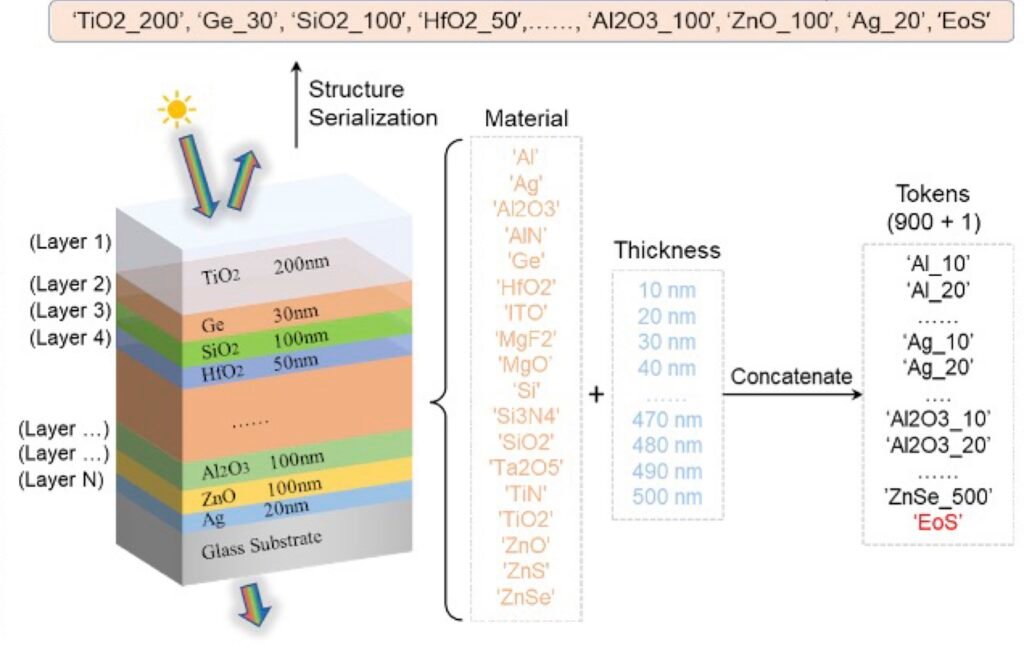
OptoGPT AI Enhances Optical Component Design Process
University of Michigan researchers have developed a new algorithm, named OptoGPT, that leverages transformer neural networks, similar to those powering large language models, to revolutionize the design of optical components. This innovation aims to streamline the creation of optical multilayer film structures, which are essential for technologies like solar cells, smart windows, and telescopes.
OptoGPT is designed to work backward, starting with desired optical properties to determine the precise material structure needed to achieve them. These multilayer films, composed of stacked thin layers of different materials, can be optimized for various functions such as maximizing light absorption in solar cells or reflection in telescopes. They are also crucial in advanced semiconductor manufacturing and in smart windows that adapt their transparency and reflectivity to regulate building temperature.
A significant advantage of OptoGPT is its speed and efficiency. It can generate designs for multilayer film structures in just 0.1 seconds, and these designs require an average of six fewer layers compared to those produced by previous methods, simplifying the manufacturing process.
L. Jay Guo, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at the University of Michigan, and the study’s corresponding author, emphasized the complexity of traditional design processes, noting that OptoGPT automates this challenging task.
The research team adapted a transformer architecture, the machine learning framework behind models like ChatGPT, for optical design. They essentially translated materials and their thicknesses into "words" recognizable by the model. By identifying correlations between these "words," OptoGPT predicts the optimal "phrase," or in this context, a design for a multilayer film structure that meets specific optical property requirements.
To validate OptoGPT’s performance, researchers compared its designs against a dataset of 1000 known structures. The difference between OptoGPT’s designs and the validation set was minimal, at only 2.58%, demonstrating high accuracy. Further fine-tuning of the designs improved accuracy to 1.92%.
Researchers also explored the inner workings of OptoGPT, mapping its decision-making processes to understand how it associates materials and thicknesses. This analysis confirmed the algorithm’s alignment with optical principles, as materials clustered logically by type and exhibited expected behaviors at minute thicknesses.
OptoGPT represents a significant advancement in inverse design algorithms, offering broader applicability compared to previous task-specific approaches. This new tool empowers researchers and engineers to efficiently design optical multilayer film structures for a wide range of applications. The research findings have been published in the journal Opto-Electronic Advances.
Try TracePro Software for design and analysis of illumination and optical systems.
-

Microscope Software Market Size, Share Report Forecasted for 2030.
The global microscope software market reached a valuation of USD 805.09 million in 2022 and is projected to expand significantly, with an anticipated compound annual growth rate of 8.03% from 2023 to 2030. Market growth is fueled by increased financial support for microscopy research and development, along with advancements in microscope and software technologies. Government funding initiatives aimed at broadening the application of microscope software in areas like precision modeling and virus imaging are also major contributors. Notably, in early 2021, the UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) announced a USD 220 million investment to enhance research infrastructure, targeting challenges including COVID-19 and environmental sustainability.
Industries are increasingly relying on digital microscopes and associated software to enhance analytical capabilities and research outcomes. These systems play a crucial role in documentation, quality assurance, research, production processes, and failure analysis across sectors including natural sciences, pharmaceuticals, medicine, aerospace, machining, and microelectronics. Keyence Corporation’s VHX-7000 series digital microscope, for example, integrates advanced analysis software and high-resolution 4K imaging, streamlining workflows by enabling high-resolution image capture and 2D and 3D measurements within a single platform, addressing limitations of traditional microscopes and SEMs.
Technological progress remains a central theme in market development, with companies actively innovating in microscope software solutions. ZEISS launched its ZEN core software suite in February 2019, featuring enhanced analysis and networking tools for automated analysis, microscope imaging, and integrated laboratory environments.
Microscope software is also facilitating research collaboration through improved data sharing. Cloud-based platforms enable researchers to securely share images and data globally, enhancing collaboration efficiency. A 2022 Wiley Analytical Science publication highlighted the OMERO microscopy image database as a valuable research data management tool, suggesting its integration into IT infrastructure for improved data handling.
The COVID-19 pandemic created a positive impact on market growth due to heightened demand for medical research and diagnostics, increasing the need for microscope software solutions. Companies invested in research, vaccine development, medical equipment, and testing solutions, further driving market activity.
Examining microscope types, electron microscopes led the market in 2022 with a 41.08% revenue share, primarily utilized in well-funded research and industrial settings due to their higher cost compared to optical microscopes. Growing collaborations between research institutions and manufacturers are expected to increase electron microscope adoption.
Scanning probe microscopes are anticipated to experience the fastest growth, used for nanoscale specimen study and atomic manipulation. Marposs introduced a software package in late 2019 to optimize machine cycle times for probe systems, potentially reducing cycle times by up to 80% while ensuring precision. Industry-driven innovation is predicted to boost microscope demand.
Optical microscopes held the second-largest market share in 2022, supported by the widespread availability of advanced optical microscopy equipment, techniques, and the relatively lower cost of optical microscope software.
In terms of software types, integrated software dominated with a 76.64% market share in 2022. Researchers favor integrated systems for their ability to combine multiple imaging techniques for comprehensive sample analysis, encompassing image processing, data analysis, and automation in a single platform. ZEISS, Nikon, and Leica Microsystems are key providers of integrated software like ZEN, NIS-Elements, and LAS X, enhancing productivity and efficiency in medical, educational, and industrial applications. Standalone software also maintained a significant market share in 2022, driven by its diverse applications across biology, materials science, and nanotechnology.
Application-wise, life sciences led the market in 2022 with a 29.14% share. Life science research utilizes compound microscopes like inverted, upright, laser microdissection, fluorescence, and digital models. Expanding applications in disease diagnosis are contributing to market growth. Increased R&D focus in neuroscience, biological sciences, semiconductors, and nanotechnology is expected to increase adoption of super-resolution microscopes, offering resolutions as fine as 10nm crucial for studying cell signaling and cancer proliferation. Nanotechnology is projected to be the fastest-growing application segment, spurred by substantial investments in nanotechnology R&D. Collaborations like JEOL Ltd.’s partnership with Digital Surf in 2018 to launch SMILE VIEW Map software for SEM systems illustrate the trend of new software-driven microscopic devices contributing to segment growth across biology, medicine, and nanotechnology.
Regionally, Asia Pacific held the largest market share in 2022 with over 36.26% revenue, and is expected to exhibit the fastest growth at a 9.22% CAGR. This is attributed to the presence of key manufacturers in Japan and increasing local manufacturers in China and India, coupled with rising demand for diagnostic centers and healthcare facilities alongside growing R&D activities. North America held a significant market share in 2022 with a strong presence of major players and high adoption of advanced microscopy systems. Companies in North America are actively advancing correlative microscopy applications. Latin America is gaining traction from pharmaceutical and biotech industries due to streamlined regulations and research infrastructure, leading to increased microscope demand. The market remains fragmented with multinational and regional companies focusing on strategies like product launches and partnerships to strengthen their market position. For instance, Oxford Instruments released Imaris 10.0 in early 2023, an advanced version of its image analysis software aimed at neuroscience applications. Key market players include Carl Zeiss AG, Leica Microsystems, Nikon Corporation, and Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
The microscope software market is segmented by application, software type, microscope type, and region, with revenue forecasts provided at regional and country levels, covering trends from 2018 to 2030.
Try TracePro Software for design and analysis of illumination and optical systems.
-

VR/AR Disappointment: Tech Underwhelms Users, Failing to Impress
Augmented and virtual reality technologies, despite decades of hype and significant investment from major companies like Apple and Meta, have yet to fully realize their potential in the market. Current market projections estimate the AR/VR market will reach $40.4 billion this year and exceed $200 billion by 2030. However, widespread adoption faces hurdles primarily related to user experience.
For virtual reality, users often encounter issues such as heavy headsets contributing to eye fatigue and headaches. The immersive experience intended often falls short due to these hardware limitations and a lack of truly compelling content. While companies have invested heavily in content creation and cost reduction for devices, the fundamental hardware problems deter sustained usage and growth. Many consumers who own VR headsets use them infrequently and for short periods due to discomfort and underwhelming experiences characterized by limited dynamic range and field of view.
Augmented reality faces even greater challenges. Current AR headsets struggle with brightness, field of view, and transparency, often failing to deliver a seamless integration of virtual and real-world content. Many devices essentially project a phone screen in front of the wearer’s eyes, resulting in virtual images that are often small, blurry, dim, and lacking in vibrant colors. This is largely attributed to limitations of conventional optical designs in modern eyewear. Companies are attempting to compensate for these hardware shortcomings by focusing on content and reducing component costs, yet the fundamental user experience limitations persist.
Researchers have developed a novel approach using anamorphic technology to address these optical challenges in both AR and VR. This new method maximizes the use of horizontal space along the eyebrow to project elongated displays through the eyewear lens, acting as a waveguide to direct images to the eye. This design promises increased brightness, improved color accuracy, and a wider field of view compared to traditional systems. Anamorphic optics can lead to lighter and more energy-efficient devices, potentially extending comfortable usage times and reducing eye strain-related headaches. Furthermore, this technology is reported to utilize readily available components and manufacturing processes, making it potentially easier for headset manufacturers to implement.
The future of AR and VR hinges on prioritizing user experience improvements alongside content development. Experts suggest that the industry needs to shift focus towards research and development of technologies that enhance the fundamental user experience. By embracing advancements like anamorphic optics and continuing to invest in related areas, AR and VR technologies can move beyond current limitations and achieve broader adoption across various sectors including education, healthcare, industry, and consumer entertainment, potentially even rendering current mobile devices obsolete in the long run.
Try TracePro Software for design and analysis of illumination and optical systems.
-

Keysight Set to Acquire Synopsys’ Optical Solutions Group
Keysight Technologies is set to acquire Synopsys’ Optical Solutions Group (OSG), a provider of optical design tools. These tools are designed to help optical engineers create advanced optics and will expand Keysight’s software portfolio into the optics and photonics domains, complementing its existing electronics design offerings. Synopsys decided to sell OSG to facilitate regulatory approval for its pending acquisition of Ansys. That larger Synopsys-Ansys transaction is expected to close in the first half of 2025 and is also subject to regulatory approvals.
Ravi Subramanian, General Manager of the Systems Design Group at Synopsys, stated that Keysight would be an “excellent future steward” for the OSG team and that the sale would benefit customers through continued competition in optical design solutions. OSG offers a range of design tools, including CODE V for imaging systems, LightTools for illumination design, LucidShape for automotive lighting, RSoft Photonic Device Tools, and ImSym, a virtual prototyping platform for imaging systems.
Niels Faché, Vice President and General Manager of Keysight Design Engineering Software, expressed enthusiasm about the acquisition, stating that it would enable Keysight to address high-performance system use cases beyond electronics, specifically in optics and photonics, given the increasing complexity of electronics design. Until the acquisition is finalized, OSG will continue its operations as part of Synopsys.
Try TracePro Software for design and analysis of illumination and optical systems.
-

Lumus Waveguide Tech Could Power Your Future Smart Sunglasses
Lumus has unveiled its latest innovation, the Z-30 binocular optical engine, designed for integration into consumer smart glasses. This new waveguide technology is presented as a significant advancement, offering a lighter and more energy-efficient solution compared to its predecessor, the Z-50.
The Z-30 boasts a weight of just 14.5 grams and is engineered to fit within the form factor of conventional eyeglasses. It delivers a resolution of 720 x 720 pixels and a 30-degree field of view, with brightness exceeding 3,000 nits per watt. Lumus highlights that the Z-30 is 50 percent lighter and smaller than the Z-50, contributing to slimmer eyewear designs and extended battery life in smart glasses.
This enhanced energy efficiency is crucial for consumer-oriented smart glasses, making them more practical for everyday use. The Z-30 optical engine leverages Lumus’ Z-Lens 2D waveguide architecture, promising superior image quality and compatibility with efficient projectors like microLEDs. The design also allows for flexible eye-box positioning, minimizes ghost effects, and supports direct bonding with prescription lenses or protective elements.
Ari Grobman, CEO of Lumus, stated that the Z-30 is specifically tailored to meet the demands of the entry-level consumer market. He emphasized that it maintains the high image quality of the Z-50 but with a narrower field-of-view to facilitate integration into standard glasses frames and improve battery performance, ultimately aiming for wider consumer adoption of smart glasses.
Lumus, an Israeli company with over two decades of experience in waveguide technology, emphasizes the superior image quality, energy efficiency, and suitability for outdoor use of its waveguides.
Try TracePro Software for design and analysis of illumination and optical systems.