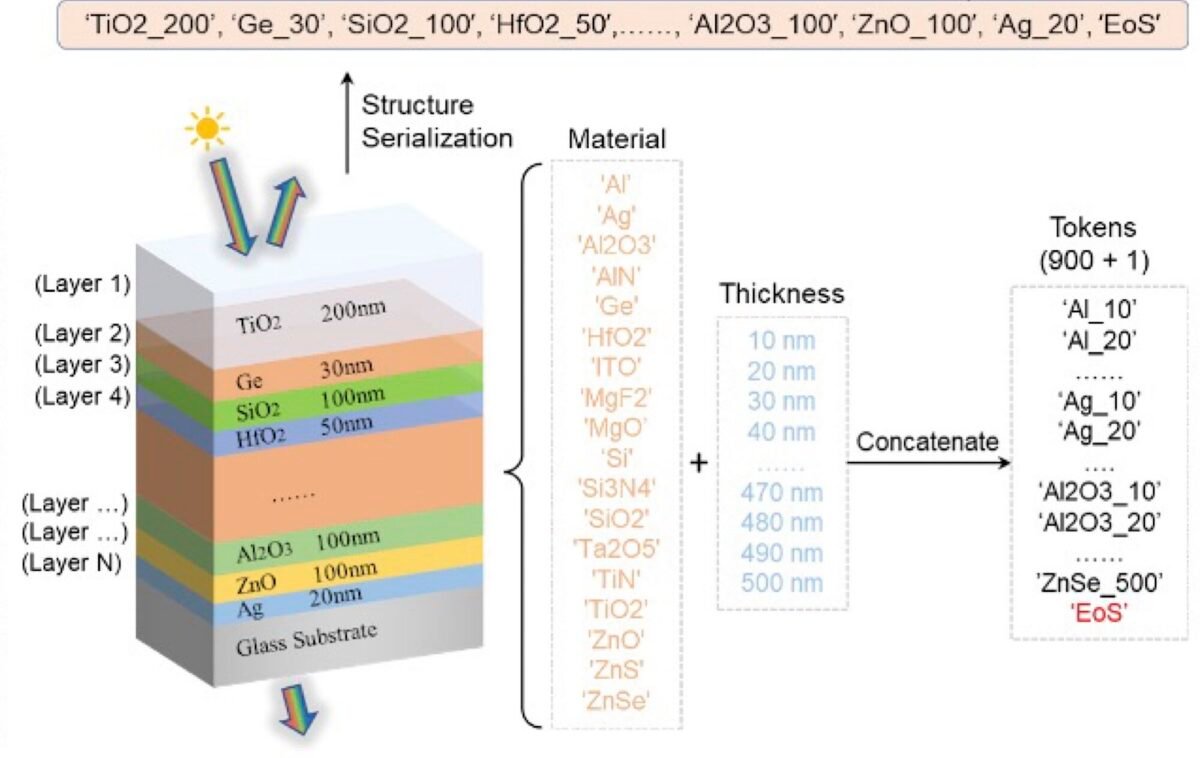
University of Michigan engineers have created a new algorithm called OptoGPT, designed to develop optical multilayer film structures for various applications, including solar cells. OptoGPT leverages the same computer architecture as the popular ChatGPT and works in reverse, determining the material structure necessary to achieve specific optical properties. This innovative algorithm can produce designs for multilayer film structures in just 0.1 seconds. These structures, composed of stacked thin layers of different materials, are crucial for maximizing light absorption in solar cells and optimizing other optical components, such as those used in telescopes. The developers of OptoGPT highlight that their designs typically require six fewer layers compared to those generated by older models, making them simpler to manufacture. L. Jay Guo, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at the University of Michigan, explained that traditional design processes are complex and require significant expertise to identify the optimal combination of materials and layer thicknesses. OptoGPT treats materials of specific thicknesses as "words" and their optical properties as inputs. By identifying correlations between these "words," the algorithm predicts the next "word" to construct a "phrase" that fulfills the desired optical property. Professor Guo, the lead author of a paper published in Opto-Electronic Advances titled “OptoGPT: A foundation model for inverse design in optical multilayer thin film structures,” stated that they essentially created artificial sentences to fit the existing ChatGPT model framework. The research paper emphasizes OptoGPT’s ability to handle the complex inverse design problem in multilayer structures and its versatility across different input targets, structure types, and fabrication processes. Although the algorithm was trained using a dataset of 10 million samples, the researchers acknowledge that this dataset represents only a fraction of the vast design possibilities for optical multilayer thin film structures. This limitation means OptoGPT may not identify designs outside of its training data. The researchers concluded that broader collaboration among research groups is necessary to develop more comprehensive models for photonic inverse design capable of handling more complex structures.
Leave a Reply